What is a vegetarian diet plan – Welcome to the world of vegetarianism! If you’re curious about what a vegetarian diet plan entails, you’re in the right place. From its definition to its nutritional benefits, food sources, meal planning, and potential challenges, this guide will provide you with a comprehensive understanding of this plant-based lifestyle.
Whether you’re considering adopting a vegetarian diet for ethical, environmental, or health reasons, this guide will equip you with the knowledge you need to make an informed decision.
Vegetarian Diet Definition
A vegetarian diet is one that is based on plant-based foods, excluding meat, poultry, fish, and seafood. There are different types of vegetarian diets, each with its own set of restrictions. Some of the most common types include:
Lacto-vegetarian Diet
Lacto-vegetarians eat dairy products, such as milk, cheese, and yogurt, but they do not eat eggs. This type of diet is often chosen by people who are allergic to eggs or who have ethical concerns about the way eggs are produced.
Ovo-vegetarian Diet
Ovo-vegetarians eat eggs, but they do not eat dairy products. This type of diet is often chosen by people who are allergic to dairy products or who have ethical concerns about the way dairy cows are treated.
Vegan Diet
Vegans do not eat any animal products, including meat, poultry, fish, seafood, dairy products, and eggs. This type of diet is often chosen by people who have ethical concerns about the way animals are treated in the food industry.
Nutritional Benefits
Embracing a vegetarian diet offers a plethora of health benefits, making it a wise choice for those seeking a healthier lifestyle. Studies have consistently shown that vegetarians have a lower risk of developing chronic diseases, such as heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer.
Essential Nutrients in Plant-Based Foods
Plant-based foods are abundant in essential nutrients that play a crucial role in maintaining optimal health. These nutrients include:
- Vitamins:Fruits, vegetables, and whole grains are excellent sources of vitamins A, C, E, and K, which are essential for various bodily functions, including immune support, vision, and bone health.
- Minerals:Plant-based foods are rich in minerals such as iron, calcium, and magnesium, which are necessary for red blood cell production, bone strength, and nerve function.
- Fiber:Fiber, found in whole grains, fruits, and vegetables, aids digestion, promotes satiety, and helps regulate blood sugar levels.
Food Sources
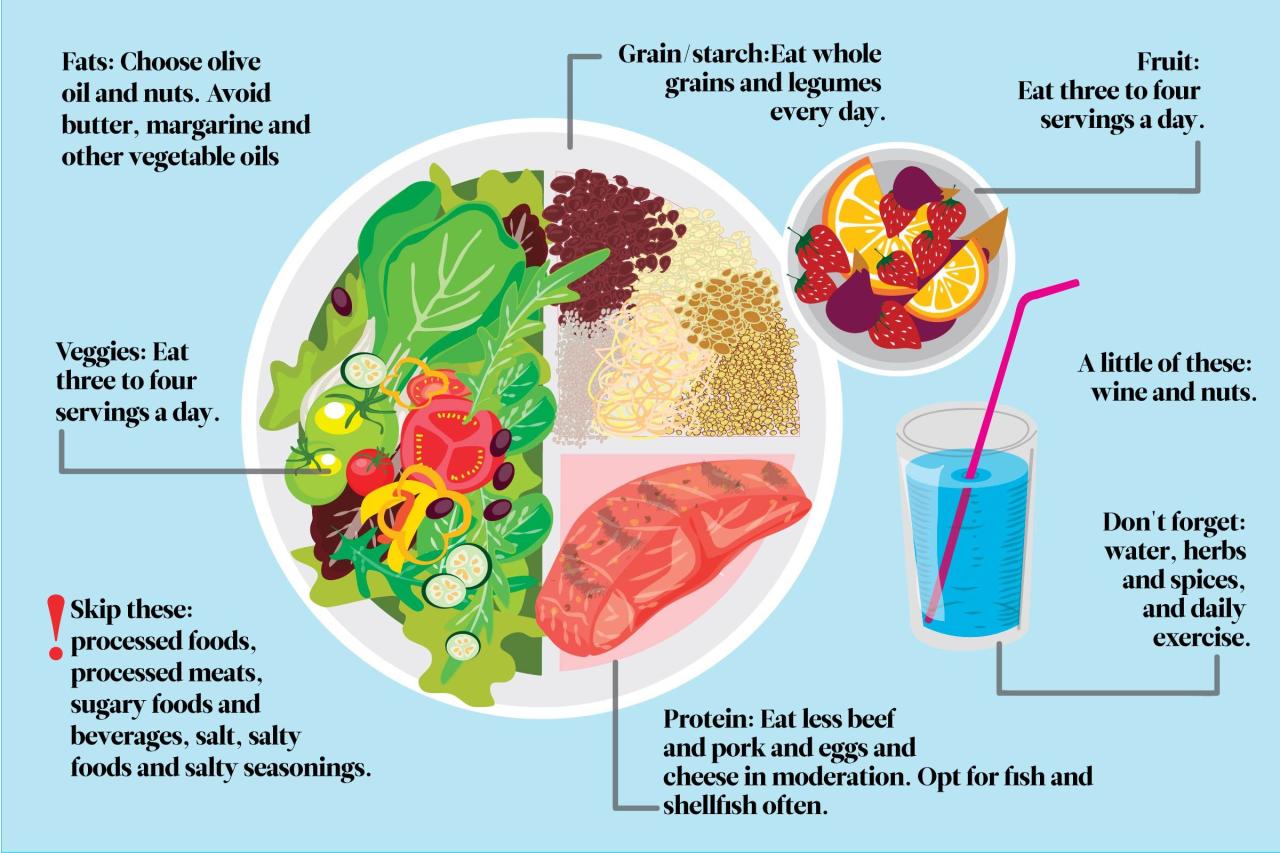
A vegetarian diet revolves around plant-based foods, offering a wide array of nutrients and health benefits. Understanding the diverse food sources available is crucial for creating a balanced and satisfying vegetarian meal plan.
Vegetarian food sources can be broadly categorized into the following groups:
Fruits
- Apples
- Bananas
- Berries (strawberries, blueberries, raspberries)
- Citrus fruits (oranges, grapefruits, lemons)
- Grapes
- Mangoes
- Pears
- Pineapples
Vegetables
- Broccoli
- Brussels sprouts
- Carrots
- Cauliflower
- Celery
- Cucumbers
- Leafy greens (spinach, kale, lettuce)
- Mushrooms
- Onions
- Potatoes
- Tomatoes
Legumes
- Beans (black beans, kidney beans, pinto beans)
- Chickpeas
- Lentils
- Peas
- Soybeans
- Tofu
- Tempeh
Nuts and Seeds, What is a vegetarian diet plan
- Almonds
- Cashews
- Chia seeds
- Flaxseeds
- Pecans
- Pumpkin seeds
- Sunflower seeds
- Walnuts
For vegetarians, ensuring adequate protein intake is essential. Plant-based protein sources include:
- Legumes (beans, lentils, chickpeas)
- Tofu and tempeh
- Nuts and seeds
- Quinoa
- Brown rice
- Edamame
By incorporating a variety of these food sources into their diet, vegetarians can meet their nutritional needs and enjoy a healthy and satisfying plant-based lifestyle.
Meal Planning
A well-structured vegetarian meal plan is essential for meeting nutrient requirements and ensuring overall health. It should provide a balanced intake of protein, carbohydrates, fats, vitamins, and minerals. Here’s a sample vegetarian meal plan that can be tailored to individual needs:
Breakfast:Oatmeal with berries, nuts, and a plant-based milk; tofu scramble with whole-wheat toast; yogurt with granola and fruit.
Men are increasingly adopting vegetarian diets for health, ethical, and environmental reasons. While some may assume that a vegetarian diet lacks essential nutrients, research shows that it can provide all the necessary vitamins and minerals for optimal health. Vegetarian diets for men offer numerous benefits, including reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, and certain types of cancer.
Lunch:Salad with grilled tempeh, quinoa, vegetables, and a light dressing; lentil soup with a side of whole-grain bread; vegetarian chili with brown rice.
Dinner:Vegetarian stir-fry with tofu, vegetables, and brown rice; pasta with marinara sauce and vegetables; black bean tacos with whole-wheat tortillas.
Snacks:Fruits, vegetables, nuts, seeds, hummus with whole-wheat pita.
Creating Flavorful and Satisfying Vegetarian Dishes
Vegetarian dishes can be just as flavorful and satisfying as meat-based meals. Here are some tips:
- Use a variety of spices and herbs to enhance flavor.
- Experiment with different cooking methods, such as grilling, roasting, or stir-frying.
- Incorporate umami-rich ingredients, such as mushrooms, soy sauce, or miso.
- Add a touch of acidity with lemon juice or vinegar to brighten flavors.
- Don’t be afraid to experiment with different textures, such as crispy, crunchy, or creamy.
Incorporating Variety and Ensuring Adequate Calorie Intake
Variety is key to a healthy vegetarian diet. Include a wide range of fruits, vegetables, whole grains, legumes, nuts, and seeds.
To ensure adequate calorie intake, include calorie-dense foods such as nuts, seeds, avocados, and olive oil. Monitor calorie intake and adjust portion sizes as needed.
Challenges and Considerations: What Is A Vegetarian Diet Plan
Embarking on a vegetarian diet offers numerous health benefits, yet it also presents potential challenges that require careful attention. Understanding these obstacles and devising practical solutions is crucial for long-term success and optimal well-being.
One of the primary concerns associated with a vegetarian diet is the risk of vitamin B12 deficiency. This essential nutrient is primarily found in animal products, and its deficiency can lead to various health issues, including fatigue, anemia, and neurological problems.
To prevent this deficiency, vegetarians must make a conscious effort to consume fortified foods, such as cereals, plant-based milk, and nutritional yeast, or consider supplementation. Regular monitoring of vitamin B12 levels through blood tests is also recommended.
Social Stigma
Another challenge that vegetarians may face is social stigma. In certain social circles, vegetarianism can be met with misunderstanding, ridicule, or even ostracism. Navigating these social dynamics requires resilience, confidence, and the ability to respectfully articulate one’s dietary choices. Joining support groups or connecting with like-minded individuals can provide a sense of community and support, fostering a positive and inclusive environment.
Importance of Professional Consultation
Before embarking on a vegetarian diet, it is imperative to consult with a healthcare professional. They can assess individual nutritional needs, provide personalized guidance, and address any specific concerns or potential risks. A healthcare professional can also recommend appropriate supplementation, if necessary, and monitor progress over time.
Final Review

In essence, a vegetarian diet plan is a way of eating that emphasizes plant-based foods while excluding or limiting animal products. It offers numerous health benefits, provides a wide range of nutrient-rich foods, and can be tailored to meet individual preferences and needs.
While there may be challenges along the way, with proper planning and support, a vegetarian diet can be a fulfilling and sustainable choice.
Query Resolution
What are the different types of vegetarian diets?
There are several types of vegetarian diets, including lacto-vegetarian (consumes dairy products), ovo-vegetarian (consumes eggs), lacto-ovo vegetarian (consumes both dairy and eggs), and vegan (excludes all animal products).
What are the health benefits of a vegetarian diet?
A vegetarian diet has been associated with a reduced risk of heart disease, stroke, certain types of cancer, and type 2 diabetes. It can also promote weight management and improve overall well-being.
How do I ensure I get enough protein on a vegetarian diet?
There are many plant-based sources of protein, including legumes (beans, lentils, peas), nuts, seeds, tofu, tempeh, and quinoa. By combining different protein sources throughout the day, vegetarians can meet their protein needs.